一、OpenFeign概念
1、OpenFeign是什么
Feign是声明性Web服务客户端。它使编写Web服务客户端更加容易。要使用Feign,请创建一个接口并对其进行注释。它具有可插入的注释支持,包括Feign注释和JAX-RS注释。Feign还支持可插拔编码器和解码器。Spring Cloud添加了对Spring MVC注释的支持,并支持使用HttpMessageConvertersSpring Web中默认使用的注释。Spring Cloud集成了Ribbon和Eureka以及Spring Cloud LoadBalancer,以在使用Feign时提供负载平衡的http客户端。
github:https://github.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-openfeign
2、干什么用的
使编写Java Http客户端更加容易
使用 RestTemplate+Ribbon 时,利用 RestTemplate 对http 请求的封装处理,形成一套模板化的调用方法,但是在实际中,由于对服务的调用可能不止一处,往往一个接口会被多处调用,所以通常都会针对每个微服务自行封装一些客户端类来包装这些依赖服务的调用。所以Feign在此基础上做了进一步封装,由他来帮助我们定义和实现服务接口的定义。在==Feign的实现下我们只需要创建一个接口并使用注解来配置它(以前是Dao接口上标注Mapper注解,现在是一个微服务接口上面标注一个Feign注解即可)==。自动封装服务调用客户端的开发量。
Feign集成了Ribbon
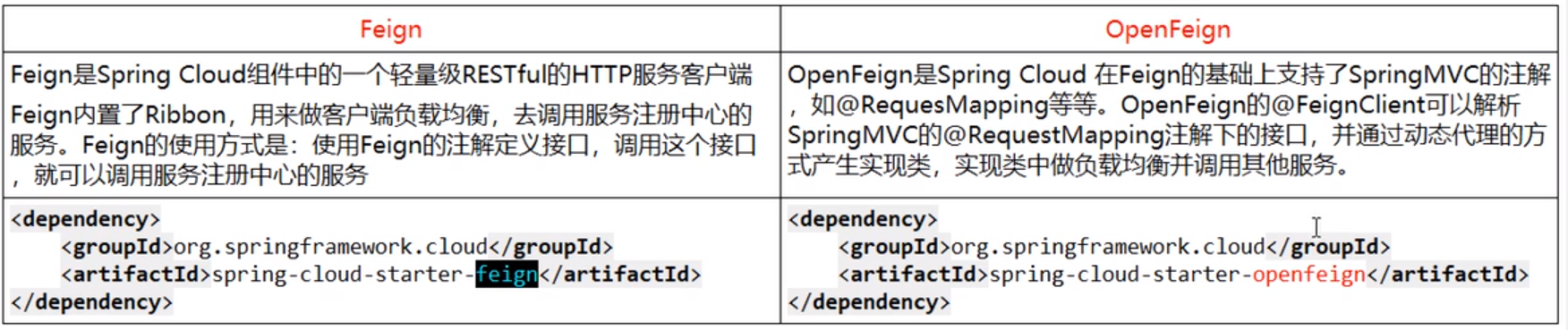
利用Ribbon维护了Payment的服务列表信息,并且实现了轮询实现客户端的负载均衡。而与Ribbon不同的是,==feign只需要定义服务绑定接口且以声明式的方法==,优雅而简单的实现服务调用。Feign与OpenFeign区别
二、OpenFeign服务接口调用步骤
1、pom依赖
<dependencies>
<!--openfeign-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--eureka client-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 引入自己定义的api通用包,可以使用Payment支付Entity -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.atguigu.springcloud</groupId>
<artifactId>cloud-api-commons</artifactId>
<version>${project.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!--web-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--一般基础通用配置-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>2、application.yml
OpenFeign默认等待1秒钟,超过后报错,YML文件里需要开启OpenFeign客户端超时控制
OpenFeign日志详细见本文末
server:
port: 80
#可以改成 Nacos
eureka:
client:
register-with-eureka: false
service-url:
defaultZone: http://eureka7001.com:7001/eureka/,http://eureka7002.com:7002/eureka/
####################### 主要配置start ###########################
#设置feign客户端超时时间(OpenFeign默认支持ribbon,超时时间默认1秒)
ribbon:
#指的是建立连接所用的时间,适用于网络状况正常的情况下,两端连接所用的时间
ReadTimeout: 5000
#指的是建立连接后从服务器读取到可用资源所用的时间
ConnectTimeout: 5000
####################### 主要配置end ##########################
logging:
level:
# feign日志以什么级别监控哪个接口(接口路径:日志级别)(需添加配置类)
com.atguigu.springcloud.service.PaymentFeignService: debug3、启动类
添加注解@EnableFeignClients,只有服务调用者开启即可(虽然建议都开)
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableFeignClients
public class FeignOrder80Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(FeignOrder80Main.class,args);
}
}4、PaymentFeignService
注意:此处@PathVariable("id")必须加“id”,不加会报错
@Component
//value为调用的微服务名
@FeignClient(value = "cloud-payment-service")
public interface PaymentFeignService {
@GetMapping(value = "/payment/get/{id}")
public CommonResult<Payment> getPaymentById(@PathVariable("id") Long id);
}@FeignClient注解详解:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface FeignClient {
/**
* 服务名称。无论是否提供url,必须为所有客户端指定名称。可以指定为属性键,例如:${propertyKey}。
*/
@AliasFor("name")
String value() default "";
/**
* 作用同上,和value二选一即可
*/
@AliasFor("value")
String name() default "";
/**
* 请求地址, 没配置的话, 会把name/value的属性值当成服务名进行调用, 配置的话则使用url的值
*/
String url() default "";
/**
* 如果存在,bean名称将使用contextId而不是name,但不会用作服务id。
* 假设一个User服务有两个FeignClient,都需要调用Product服务, 因为name属性值一样,
* 所以需要通过配置contextId来区分,否则启动项目时会报错
*/
String contextId() default "";
/**
* path定义当前FeignClient访问接口时的统一前缀,比如接口地址是/user/get,
* 如果你定义了前缀是user, 那么具体方法上的路径就只需要写/get 即可。
*/
String path() default "";
/**
* configuration是配置Feign配置类,
* 在配置类中可以自定义Feign的Encoder、Decoder、LogLevel、Contract等。
*/
Class<?>[] configuration() default {};
/**
* fallback定义容错的处理类,也就是回退逻辑,fallback的类必须实现Feign Client的接口
* fallback的类必须是Spring的Bean
* 无法知道熔断的异常信息。
*/
Class<?> fallback() default void.class;
/**
* fallback定义容错的处理类,也就是回退逻辑,fallback的类必须实现Feign Client的接口
* fallback的类必须是Spring的Bean
* 可以知道熔断的异常信息。
*/
Class<?> fallbackFactory() default void.class;
/**
* 当我们的fallback实现了Feign后,也就意味着FeignClient有多个相同的Bean在Spring容器中,
* 当我们在使用@Autowired进行注入的时候,不知道注入哪个,
* 所以我们需要设置一个优先级高的,@Primary注解就是干这件事情的。
* 一般不需要改
*/
boolean primary() default true;
/**
* 目前serviceId已经废弃了,直接使用name即可。
*/
@Deprecated
String serviceId() default "";
/**
* @return the <code>@Qualifier</code> value for the feign client.
*/
String qualifier() default "";
/**
* @return whether 404s should be decoded instead of throwing FeignExceptions
*/
boolean decode404() default false;
}示例
@FeignClient(contextId = "PlatformParkService",
value = "nlp-platform",
url = "${platform.url:}", // http://127.0.0.1:8082
path = "/api-platform"
configuration = FeignHttpClientProperties.class,
fallbackFactory = PlatformParkService.PlatformParkServiceFallbackFactory.class)
public interface PlatformParkService {
@PostMapping("/api/openapi/park/syncPark")
Result syncPark(@RequestBody String dispatchOrderJson);
@PostMapping("/api/openapi/park/syncCancelPark")
Result syncCancelPark(@RequestBody String dispatchOrderJson);
@Component
class PlatformParkServiceFallbackFactory implements FallbackFactory<PlatformParkService> {
@Override
public PlatformParkService create(Throwable throwable) {
return new PlatformParkService() {
@Override
public Result syncPark(String dispatchNo) {
return null;
}
@Override
public Result syncCancelPark(String dispatchOrderJson) {
return null;
}
};
}
}
}5、OrderFeignController
@RestController
@Slf4j
public class OrderFeignController {
@Resource
private PaymentFeignService paymentFeignService;
@GetMapping(value = "/consumer/payment/get/{id}")
public CommonResult<Payment> getPaymentById(@PathVariable("id") Long id)
{
return paymentFeignService.getPaymentById(id);
}
}
三、OpenFeign日志
(1)日志级别
- NONE:默认不显示日志
- BASIC:仅记录请求方法,URL,响应状态及执行时间
- HEADERS:除了BASIC中定义的信息之外,还有请求和响应的头信息
- FULL:除了HEADERS中定义的信息外,还有请求和响应的正文及元数据
(2)配置类
@Configuration
public class FeignConfig {
@Bean
Logger.Level feignLoggerLevel(){
//配置日志级别
return Logger.Level.FULL;
}
}(3)application.yml
logging:
level:
# 选择具体接口的日志输出 级别为debug
com.wxh.springcloud.service.PaymentFeignService: debug四、feign拦截器
微服务之前调用的时候请求不会传递参数,通过实现 RequestInterceptor 接口,完成对所有的Feign请求,传递请求头和请求参数。
RequestInterceptor 接口定义了apply方法,其参数为RequestTemplate;它有一个抽象类为BaseRequestInterceptor,还有几个实现类分别为
BasicAuthRequestInterceptor:实现了RequestInterceptor接口,其apply方法往RequestTemplate添加名为Authorization的headerFeignAcceptGzipEncodingInterceptor:继承了BaseRequestInterceptor,它的apply方法往RequestTemplate添加了名为Accept-Encoding,值为gzip,deflate的headerFeignContentGzipEncodingInterceptor:继承了BaseRequestInterceptor,其apply方法先判断是否需要compression,即mimeType是否符合要求以及content大小是否超出阈值,需要compress的话则添加名为Content-Encoding,值为gzip,deflate的header
BaseRequestInterceptor:定义了addHeader方法,往requestTemplate添加非重名的header
自定义
获取前端传递的token,并在添加到 feign 的请求中
@Slf4j
@Configuration
public class FeignConfig implements RequestInterceptor {
private final FeignParamConfig config;
private static AntPathMatcher antPathMatcher = new AntPathMatcher();
public FeignConfig(FeignParamConfig config){
this.config = config;
}
@Override
public void apply(RequestTemplate requestTemplate) {
String feignUrl = requestTemplate.url();
for (String patten : config.getIgnoreUri()) {
if (antPathMatcher.match(patten,feignUrl)){
return;
}
}
log.debug("auth feign interceptor url : {}" ,feignUrl);
ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
log.debug("client feign bean attributes is null ? {}", Objects.isNull(attributes));
if (Objects.isNull(attributes)){
return;
}
HttpServletRequest request = attributes.getRequest();
log.debug("auth request url : {}",request.getRequestURL());
// 设置token
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(request.getHeader("token"))){
requestTemplate.header("token",request.getHeader("token"));
}
}
}@Data
@Configuration
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = FeignParamConfig.PREFIX)
public class FeignParamConfig {
public static final String PREFIX = "rewind.feign.ignore";
/*
* Feign 请求过滤白名单
* */
private List<String> ignoreUri = new ArrayList<>();
@Deprecated
private List<String> instanceName = new ArrayList<>();
}五、Header丢失问题
1、Header丢失
1、使用Headers注解。直接在请求上或者在类上添加
2、通过实现RequestInterceptor接口,完成对所有的Feign请求,设置Header
如《四、feign拦截器》的案例
2、异步调用丢失
// RequestContextHolder实际上是一个ThreadLocal,在异步进行feign远程调用时,无法获取到请求线程的header,所以需要手动设置
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes =
(ServletRequestAttributes)RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
// 异步回调
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(()->{
//手动设置header
RequestContextHolder.setRequestAttributes(requestAttributes);
// 业务代码
...
});
String result = completableFuture.get(); // 获取阻塞执行结果
System.out.println(result);添加Header的方式
1、RequestMapping设置
在application.yml中配置
app.secret: appSecretVal编写feignClient
@PostMapping(value = "/book/api", headers = {"Content-Type=application/json;charset=UTF-8", "App-Secret=${app.secret}"})
void saveBook(@RequestBody BookDto condition);2、@RequestHeader
设置单个header属性
@GetMapping(value = "/getStuDetail")
public StudentVo getStudentDetail(@RequestBody StudentDto condition, @RequestHeader("Authorization") String token);设置多个header属性
@PostMapping(value = "/card")
public CardVo createCard(@RequestBody CardDto condition, @RequestHeader MultiValueMap<String, String> headers);查看源码 org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestHeader 说明:If the method parameter is Map<String, String>, MultiValueMap<String, String>, or HttpHeaders then the map is populated with all header names and values.

